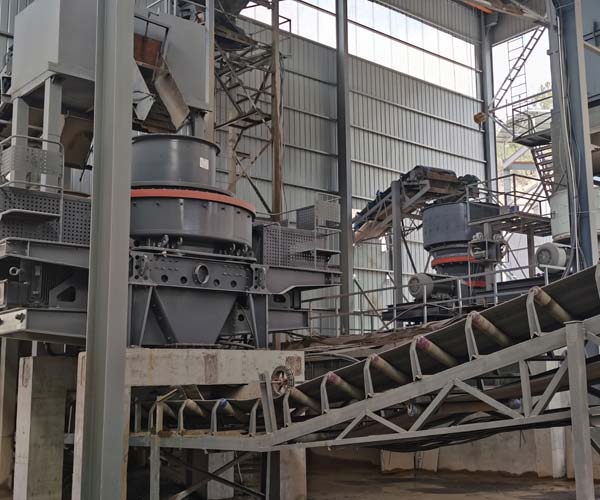
Rock crusher machines are the unsung heroes of the construction and related industries. They are the workhorses behind the scenes, breaking down unwieldy rocks into manageable pieces that serve as the foundation for infrastructure development.
24 Online Service
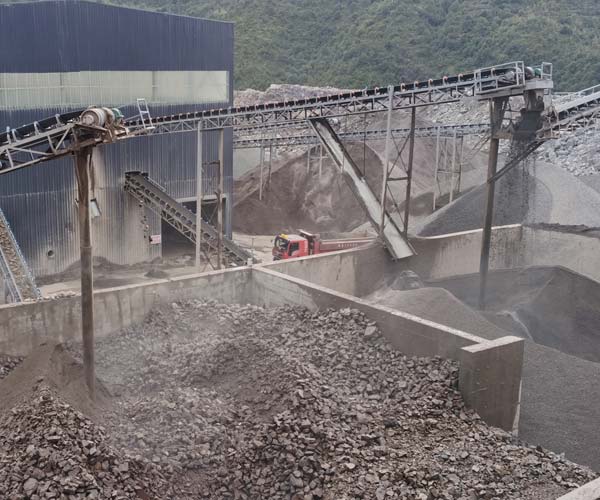

Aggregates are granular materials used as a base for the construction of roads, buildings, bridges, and many other structures. They consist of particles that are typically derived from natural sources like rock, gravel, sand, or recycled materials. These materials are processed and sorted into various sizes to meet the specific requirements of construction projects. Aggregates serve as the backbone of concrete, asphalt, and other construction materials.
There are various types of aggregates, each with distinct characteristics and applications in construction and various industries. The primary types of aggregates include:
Definition: Crushed stone is a type of construction aggregate produced by mechanically crushing large rocks into smaller pieces.
Uses: Crushed stone is a versatile material used in a wide range of construction applications. It is a key component in concrete, asphalt, and road base. Crushed stone is used for everything from road construction and foundation building to landscaping and drainage systems.
Definition: Sand is a naturally occurring granular material composed of small mineral and rock particles.
Uses: Sand is an essential component of concrete and mortar. It is used in various construction projects, including the creation of plaster, stucco, and for backfilling utility trenches. In addition to construction, sand plays a role in manufacturing glass, casting metals, and foundry work.
Definition: Gravel is a coarse aggregate consisting of small rock fragments or pebbles.
Uses: Gravel is frequently used in road construction as a base material. It provides excellent drainage properties, making it suitable for use in drainage systems and for creating permeable surfaces. Gravel is also employed in landscaping, as it offers an aesthetically pleasing and practical option for pathways and driveways.
Definition: Recycled aggregates are derived from the processing of waste construction materials, such as crushed concrete and reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP).
Uses: Recycled aggregates have gained popularity due to their environmental benefits. They are used in various construction applications, including road construction, as a replacement for aggregates. Recycled aggregates help reduce the depletion of natural resources and minimize waste disposal.
Definition: Lightweight aggregates are materials that are lighter in weight than traditional aggregates, often produced from materials like expanded clay, shale, or slag.
Uses: Lightweight aggregates are used in applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in the production of lightweight concrete blocks, insulating concrete, and precast concrete products. They help improve the thermal and acoustic properties of construction materials.
Definition: Marine aggregates are extracted from the seabed and used in coastal protection, beach nourishment, and offshore construction projects.
Uses: These specialized aggregates are vital in coastal engineering to mitigate erosion and protect coastlines. They also find use in underwater construction projects, such as the building of artificial reefs and offshore installations.

When we think about the construction industry, it’s easy to envision towering skyscrapers, expansive highways, and intricate bridges. However, behind the scenes, there’s a critical process that often goes unnoticed but is absolutely essential for making these projects a reality – the crushing of rocks. Rock crusher machines play a crucial role in the aggregate production process, as they are the workhorses that transform large, unwieldy rocks into smaller, manageable pieces that can be used in construction and a multitude of other applications.
Aggregate is a term used in the construction industry to describe a range of materials, such as sand, gravel, crushed stone, and other mineral-based resources. These materials are the fundamental building blocks of infrastructure development. Whether it’s creating a stable foundation for a building, laying the base for a road, or forming the structural components of a bridge, aggregates are the unsung heroes of construction.
Rocks are naturally occurring aggregates. They come in all shapes and sizes, from pebbles to boulders, and they need to be processed before they can be effectively used in construction. This is where rock crusher machines come into play. The primary objective of these machines is to break down large, unmanageable rocks into smaller pieces of uniform size, known as crushed stone or gravel. There are several key reasons for this crushing process:
Rocks in their natural state are irregular in shape and size. In construction, consistency is critical. By crushing rocks into uniform pieces, we ensure that the final product is more predictable, making it easier to work with and providing a smoother finish to the structures.
Crushed rocks are more compact and interlock better, which enhances the structural integrity of concrete and asphalt mixtures. This results in stronger, more durable construction materials, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and repairs.
Smaller, crushed rocks are easier to transport, reducing transportation costs. Moreover, by processing rocks on-site with portable rock crushers, construction projects can minimize transportation expenses and reduce their carbon footprint.
Utilizing crushed rocks helps preserve natural resources. Rather than mining new rocks, which can be environmentally damaging, the recycling of existing rock materials through crushing is a more sustainable approach.
Rock crushers allow for the production of various sizes and types of crushed rock, catering to the specific requirements of different construction projects. This customization is essential in meeting the diverse demands of the construction industry.
Rock crusher machines come in various types, each designed to tackle specific rock crushing tasks. Here are some common types:
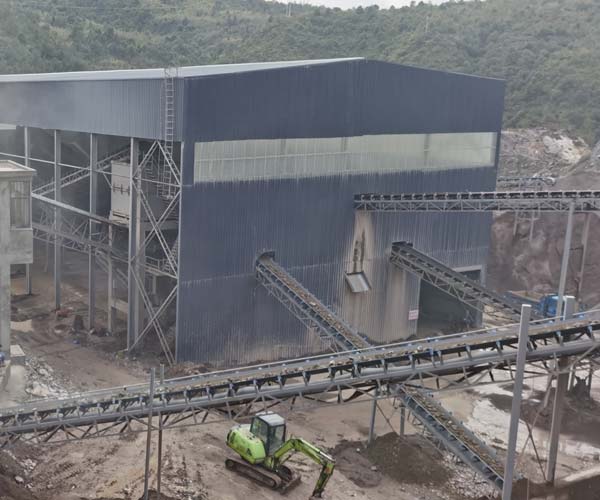

The crushing process is a fundamental operation in various industries, from construction to mining, that transforms large rocks into valuable aggregate materials. This seemingly simple task involves a meticulously orchestrated series of steps that ensure the production of high-quality materials.
The journey begins with the raw material, often large rocks or boulders, which are excavated from quarries or mines. These rocks are initially subjected to primary crushing, which is typically achieved using a jaw crusher. A jaw crusher operates by exerting force on the rock, breaking it into smaller, manageable pieces. The primary crusher reduces the rock size to roughly 6-10 inches in diameter, making it more manageable for subsequent processes.
After the primary crushing, the rock fragments are further refined in the secondary crushing stage. This process employs equipment like cone crushers or impact crushers, which specialize in reducing the size of the rock to smaller, more uniform pieces, usually around 1-2 inches in diameter. The choice of secondary crusher depends on factors such as the required final product size and the properties of the rock.
Once the rock has undergone secondary crushing, the tertiary crushing phase comes into play. This is the final stage of the transformation process. Tertiary crushers, which can be cone crushers or vertical shaft impact crushers, reduce the rock to the desired size, typically in the range of 3/8 to 1 inch. The result is aggregate material with precise specifications that can meet the requirements of various applications.
To ensure that the crushed material meets specific quality standards, it often goes through a screening and sorting process. This involves passing the material through a series of screens with varying mesh sizes to separate it into different grades based on size. This meticulous sorting ensures that the end product is consistent and free from oversized or undersized particles.
Depending on the application, some crushed aggregates may undergo washing to remove impurities and contaminants. This is especially important when the aggregates will be used in concrete production, as impurities can compromise the quality and durability of the final product. Final processing may also involve further refinement steps like crushing, grinding, or shaping to meet specific requirements.
The construction industry is one of the largest consumers of crushed aggregate. These materials are used in various construction projects, from road and highway construction to building foundations and concrete production. Aggregates serve as the essential building blocks for creating durable and stable structures. They enhance the strength and durability of concrete, making it the most widely used construction material worldwide.
Crushed aggregate plays a pivotal role in the construction and maintenance of road networks and other infrastructure projects. In road construction, aggregates are used for sub-base, base, and surface layers, providing the necessary strength and stability to withstand the rigors of heavy traffic. The choice of aggregate type and size is critical in ensuring the longevity and performance of road surfaces.
The production of concrete relies heavily on aggregates, with sand, gravel, and crushed stone constituting a significant portion of the mix. Aggregates provide the necessary structural support and workability to concrete, making it versatile for various applications, from simple sidewalks to towering skyscrapers.
Crushed aggregate is used as railway ballast, the foundation that supports and stabilizes railroad tracks. The uniformity and durability of aggregates are crucial to maintaining the safety and efficiency of rail transportation systems.
In water-related projects, crushed aggregates are employed in the construction of reservoirs, dams, and filtration systems. They provide a solid foundation and assist in proper drainage and water management.
Beyond their structural and functional roles, crushed aggregates find applications in landscaping and decorative purposes. They can be used for pathways, garden borders, and decorative elements in urban design, enhancing the aesthetics of outdoor spaces.
Various industries, including manufacturing and mining, utilize crushed aggregates for diverse purposes. They are used as fill material, in the production of refractory materials, and in the manufacturing of various products like ceramics, glass, and chemicals.
In agriculture, crushed aggregates are employed for various purposes, such as creating driveways, paths, and foundations for farm buildings. They also aid in soil stabilization and erosion control.
Crushed aggregates are critical in erosion control and drainage systems. They can be used to stabilize soil and prevent erosion in areas susceptible to water runoff, such as construction sites or slopes.
Our Projects
Copyright © ZENITH, All Right Reserved.