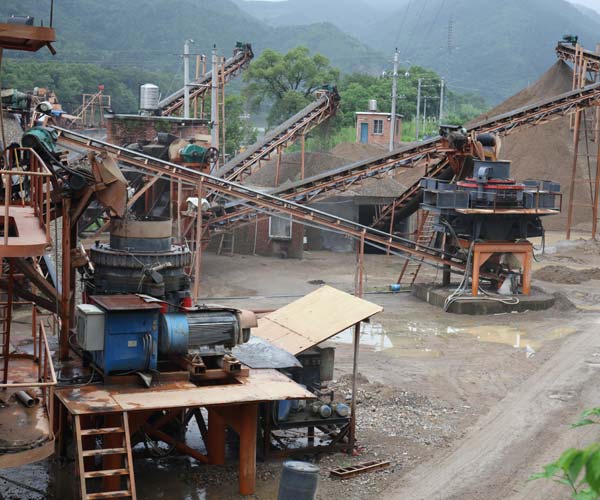
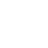
The artificial sand manufacturing process encapsulates a symphony of intricate steps, where raw materials transform into a valuable construction resource. By replicating the natural geological processes that create sand, manufacturers have unlocked a sustainable alternative to traditional sand extraction.
24 Online Service

As concerns about environmental sustainability and resource scarcity grow, industries are turning to innovative alternatives to traditional materials. One such innovation that has gained prominence is artificial sand, a man-made replacement for natural sand in construction activities.
Artificial sand, often referred to as manufactured sand or crushed sand, is a product derived from crushing rocks and stones. Unlike naturally occurring sand, which is usually obtained from riverbeds and beaches, artificial sand is produced through mechanical processes that involve crushing, screening, and sometimes further processing. The result is a granular material that possesses similar properties to natural sand and can be used in a variety of construction applications.
Artificial sand is typically composed of finely crushed rocks, minerals, and other aggregates. The exact composition can vary depending on the source materials and the specific production processes involved. Common materials used in the production of artificial sand include crushed rocks such as granite, limestone, and basalt. These rocks are subjected to crushing and screening to produce particles of the desired size and shape. Additionally, certain industrial by-products and waste materials, such as quarry dust, can also be used as a partial replacement for natural sand in the manufacturing process.
Artificial sand finds application in a wide range of construction activities, including:
Concrete Production: Artificial sand is a key ingredient in concrete manufacturing, where it acts as a fine aggregate. It contributes to the strength, durability, and workability of concrete mixes.
Mortar: In mortar production, artificial sand can replace natural sand, enhancing the properties of the mortar mix used for masonry and plastering work.
Asphalt Mixes: Artificial sand can be used in asphalt mixes for road construction, providing improved durability and performance.
Land Reclamation: In areas prone to erosion or coastal degradation, artificial sand can be used for beach nourishment and land reclamation projects.
Pre-cast Concrete Products: Artificial sand is also used in the production of pre-cast concrete products such as bricks, blocks, and pipes.
The production of artificial sand involves the use of various materials, primarily crushed rocks, to achieve the desired properties. Rocks like granite, limestone, and basalt are commonly used due to their durability, hardness, and availability. These rocks are crushed to specific particle sizes using crushers and then screened to ensure uniformity. Additionally, industrial by-products such as quarry dust and recycled concrete aggregate can be incorporated to supplement the primary materials.
Maintaining consistent quality is crucial in the production of artificial sand to ensure that it meets the required industry standards. Quality control involves careful monitoring of the raw materials, production processes, and the final product. Particle size distribution, shape, texture, moisture content, and impurity levels are some of the parameters that need to be monitored and controlled.
Standardization is equally important, as it ensures that the artificial sand produced by different manufacturers possesses the same essential properties. This promotes uniformity in construction materials and allows engineers and builders to confidently design and construct structures using artificial sand.
In an era where sustainable resource management takes precedence, the demand for construction materials has intensified the search for alternatives. One such innovation is the creation of artificial sand, a process that mimics nature’s meticulous craftsmanship to produce high-quality construction material.
The journey of artificial sand begins with the careful selection of raw materials. Natural sand is predominantly composed of fine-grained minerals like quartz and feldspar, which are broken down by natural forces over time. Mimicking this natural process, manufacturers opt for hard, durable rocks that can be crushed into desired particle sizes. These rocks are selected based on factors such as hardness, particle shape, and mineral composition.
The chosen rocks are then subjected to preliminary processing, involving tasks like removing impurities and segregating different sizes. Specialized crushers break down the large rocks into smaller fragments, maintaining a controlled particle size distribution. This preliminary step ensures the consistency of the artificial sand’s final product, thereby contributing to the overall quality of construction projects.
The heart of the artificial sand manufacturing process lies in the crushing and screening stage. Specialized machinery, including jaw crushers, gyratory crushers, and impact crushers, perform the crucial task of breaking down the raw materials into smaller, manageable sizes. These machines apply tremendous force to the rocks, causing them to fracture along natural lines.
Following the crushing phase, the fragmented materials are screened to achieve a uniform particle size distribution. Vibrating screens and sieves, equipped with different mesh sizes, separate the crushed particles into various categories. This classification ensures that the artificial sand closely resembles the gradation of natural sand, meeting industry standards and specific project requirements.
The next phase of the artificial sand manufacturing process involves washing and grading the crushed materials. Washing plays a vital role in eliminating impurities, such as clay, silt, and dust, which may compromise the sand’s quality. Log washers and sand screws are commonly used for this purpose, ensuring that the final product is free from contaminants that could adversely affect concrete strength and durability.
Grading, on the other hand, involves separating the washed sand into different size fractions. This step is essential to achieve the desired mix of particle sizes that suit various construction applications. Modern air classifiers and hydrocyclones facilitate accurate grading, contributing to the consistency of the artificial sand.
In some cases, achieving specific particle shapes becomes imperative for certain construction projects. To cater to these requirements, manufacturers employ shaping techniques. Vertical shaft impactors (VSIs) and high-speed cone crushers play a pivotal role in shaping the particles. These machines utilize high-speed rotation to reshape the particles into desired angular and cubical shapes, enhancing the sand’s mechanical properties and workability.
The artificial sand manufacturing process is heavily reliant on advanced machinery and equipment, which execute each stage with precision and efficiency. Crushers, screens, washers, and classifiers are specifically designed to handle the unique challenges posed by the production of artificial sand. These machines are equipped with robust components, wear-resistant materials, and intelligent control systems that ensure optimal performance and minimal downtime.
The machinery involved in the artificial sand manufacturing process is a testament to the amalgamation of engineering prowess and innovative technology. The synchronized functioning of these machines ensures that the final product adheres to the stringent quality standards set by the construction industry.

Starting a new business is an exciting endeavor that requires careful planning and strategic thinking. Whether you’re venturing into manufacturing and sales or providing specialized services, a well-thought-out business plan is crucial for your success.
Market research is the foundation of a successful business. It involves gathering and analyzing information about your industry, competitors, and potential customers. This step provides valuable insights that will help you make informed decisions throughout the planning and setup process.
Begin by researching the industry you’re entering. Understand the current trends, growth potential, and challenges. Identify key players in the industry and analyze their strengths and weaknesses.
Study your competitors to identify what sets your business apart. Analyze their products, pricing strategies, marketing approaches, and customer reviews. This information will help you position your business effectively in the market.
Clearly define your target audience. Who are your potential customers? What are their preferences, needs, and pain points? Tailor your products or services to meet these requirements.
Assess the demand for your offerings. Is there a viable market for your products or services? What is the potential growth rate? Understanding the market size will influence your production or service capacity.
Selecting the right business model is crucial as it defines how your business will generate revenue and create value. Depending on your chosen path, you could either focus on manufacturing and selling a tangible product or providing specialized services. Let’s explore both options:
If you decide to venture into the production and sale of sand, consider the following steps:
Evaluate the availability and quality of sand in your chosen location. Identify potential sources and ensure a sustainable supply.
Determine the machinery, equipment, and facilities required for sand extraction, processing, and packaging. Calculate the initial investment and ongoing operational costs.
Plan how you will distribute your sand to customers. Explore transportation options, such as trucks or bulk shipping, and establish distribution networks.
Implement rigorous quality control measures to ensure that the sand meets industry standards and customer expectations.
If your focus is on providing sand manufacturing services, follow these steps:
Invest in the technology and expertise required to manufacture sand. This could involve advanced crushing, screening, and shaping techniques to create sand from various raw materials.
Define the specific services you will provide. Will you cater to specific industries or offer a wide range of sand types?
Build relationships with construction companies, manufacturers, and other potential clients who require high-quality manufactured sand.
Clearly communicate the benefits of your manufactured sand over naturally occurring sand, such as consistent quality and reduced environmental impact.
Navigating the legal and regulatory landscape is essential to ensure your business operates compliantly and ethically. Here are some key considerations:
Choose a suitable legal structure for your business, such as a sole proprietorship, partnership, limited liability company (LLC), or corporation. Each structure has different legal, tax, and liability implications.
Research and obtain the necessary permits and licenses to operate in your industry. Depending on your location and business model, this could include environmental permits, zoning approvals, and health and safety certifications.
Manufacturing businesses often have environmental implications. Develop strategies to minimize your ecological footprint and comply with environmental regulations.
Intellectual Property:
If you have developed unique processes or technologies for sand manufacturing, consider protecting your intellectual property through patents or trade secrets.
Choosing the right location for your manufacturing facility is a critical decision that impacts your operational efficiency and accessibility to suppliers and customers. Consider the following factors:
If your business relies on natural resources like sand, select a location close to the source to minimize transportation costs.
Assess the availability of highways, railways, and ports for efficient distribution of your products.
Choose a location with access to a skilled workforce familiar with the manufacturing processes you’ll employ.
Ensure the chosen location is zoned for your type of business and complies with local regulations. This includes environmental and safety considerations.
Evaluate the proximity to your target market. A location that provides easy access to customers can reduce delivery times and costs.
Our Projects
Copyright © ZENITH, All Right Reserved.