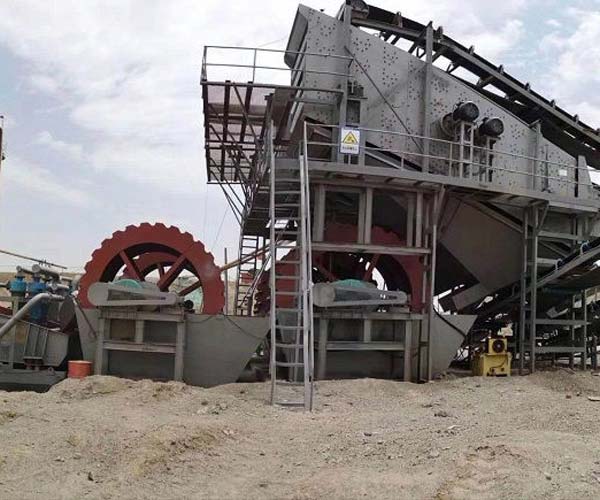
Coal washing equipment has come a long way in meeting the demands of an ever-changing energy landscape. Designing a coal washing plant is a multifaceted task that requires a thorough understanding of coal characteristics, process engineering, and equipment selection.
24 Online Service

The utilization of raw coal directly from mines poses numerous challenges due to the presence of impurities. Coal washing, a process aimed at separating impurities from raw coal, is a crucial step to enhance energy efficiency, improve combustion, and reduce environmental impact.
These impurities can be broadly categorized into inorganic and organic matter. Inorganic impurities include rock, clay, shale, and other mineral substances, while organic impurities encompass sulfur, nitrogen, ash, and trace elements. The presence of these impurities significantly impacts the overall quality of the coal and its combustion efficiency.
Raw coal with high levels of impurities has lower energy content per unit mass, leading to reduced energy efficiency in power generation and industrial applications. This directly translates to increased consumption and higher greenhouse gas emissions.
Burning raw coal releases harmful pollutants such as sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter, contributing to air pollution and smog formation. These pollutants have severe implications for human health and the environment.
When raw coal is used without proper cleaning, it can result in water pollution through the leaching of harmful minerals and contaminants into surrounding water bodies.
The presence of impurities in raw coal leads to increased wear and tear on equipment and infrastructure, raising maintenance costs and reducing the overall lifespan of machinery.
One of the most significant impurities in coal is sulfur, which is primarily responsible for the formation of sulfur dioxide during combustion. SO2 is a major contributor to acid rain and poses serious health risks when inhaled.
Ash is the residue left after coal combustion and contains various metallic elements. It hampers the efficiency of boilers and other combustion equipment, leading to increased energy consumption and maintenance costs.
Nitrogen compounds in coal produce nitrogen oxides during combustion, contributing to smog formation and air pollution.
Some trace elements, such as mercury and arsenic, are highly toxic and can be released into the atmosphere when coal is burned, leading to environmental contamination and health hazards.
Coal washing significantly reduces the levels of sulfur and other harmful pollutants, leading to a substantial decrease in emissions of sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. This results in cleaner air and improved public health.
Coal washing not only improves the quality of coal for combustion but also reduces the leaching of harmful minerals and contaminants into water bodies. This helps in preserving aquatic ecosystems and safeguarding drinking water sources.
By removing impurities, coal washing increases the energy content of coal, leading to improved combustion efficiency. This means that less coal is required to produce the same amount of energy, ultimately reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Effective coal washing ensures better utilization of coal resources, making it more sustainable for future generations. It also reduces the need for wasteful practices like “coal blending,” where low-quality coal is mixed with higher-grade coal to meet specifications.
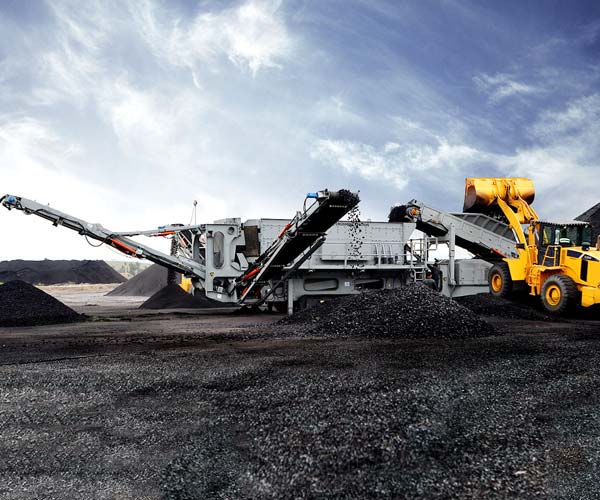

Coal washing plants play a vital role in enhancing the quality of coal, ensuring it meets the required specifications for various industries while also addressing environmental concerns.
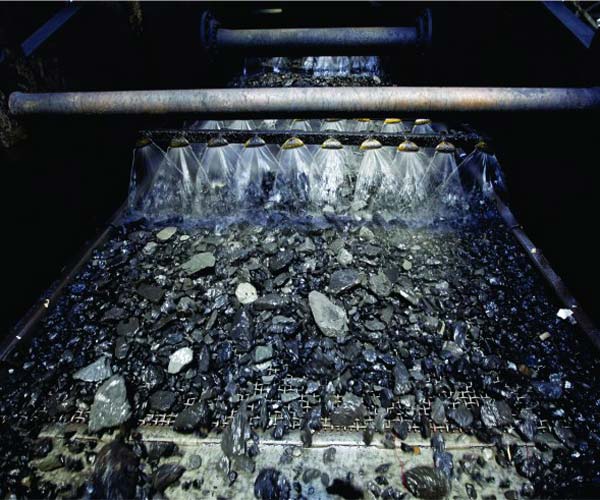
The first step in the coal washing process is the preparation of raw coal by using crushing and screening equipment. The extracted coal from the mines often contains large rocks, dirt, and other impurities that need to be removed before the actual washing process. Crushing equipment, such as crushers and hammer mills, is employed to reduce the size of coal to manageable levels. This not only makes the coal more suitable for washing but also ensures a consistent size, which is essential for efficient and effective processing.
After crushing, the coal is further screened to segregate it into different size fractions. Screening equipment, like vibrating screens, helps separate coal particles based on their sizes, allowing for more precise washing and effective removal of impurities. The combination of crushing and screening equipment ensures that the coal is properly prepared for the washing process, optimizing its quality and overall performance.
Coal remains one of the world’s most widely used energy sources, and as environmental concerns grow, the need for efficient coal washing techniques becomes increasingly important. Coal washing equipment plays a crucial role in separating impurities from coal and ensuring a cleaner and more efficient combustion process. Over the years, various types of coal washing equipment have been developed to meet the diverse needs of the coal industry.
The Dense Medium Cyclone (DMC) is a widely used coal washing equipment that utilizes a dense medium, typically a suspension of magnetite or ferrosilicon, to separate coal from its impurities. This cyclone-based separation process relies on the difference in density between coal and impurities. The feed coal is introduced to the cyclone at a high velocity, and the swirling action separates the coal from lighter materials, which are then discharged as waste.
The jig washer is another commonly used coal washing equipment that relies on the principle of gravity separation. It consists of a series of compartments or ‘jigs’ where coal is placed and agitated with water. The heavier coal particles settle faster than the lighter impurities, allowing for effective separation.
Froth flotation is a well-established coal washing technique that relies on the selective attachment of air bubbles to coal particles. In this process, the coal is mixed with water and various reagents to create a frothy mixture. The coal particles attach to the bubbles and rise to the surface, where they can be collected, leaving the impurities behind.
The Dense Medium Vessel (DMV) is a newer development in coal washing technology. It is similar to the Dense Medium Cyclone but operates in a larger vessel, allowing for more precise control over the separation process. The DMV can handle a wider range of coal sizes and has the flexibility to adjust the density of the medium during the operation.
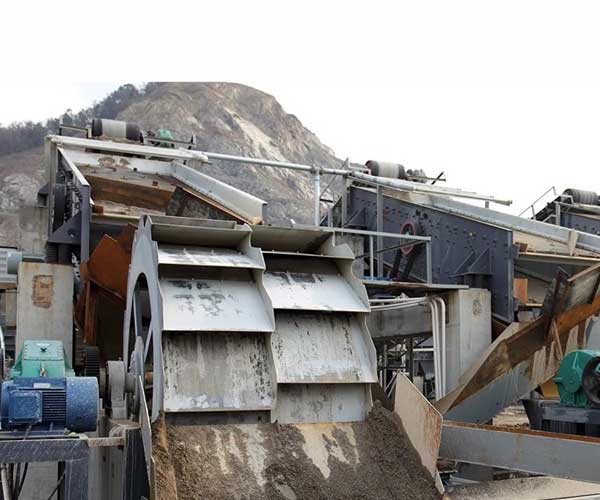

The process of coal washing, also known as coal preparation, is crucial in extracting high-quality coal from raw mined coal. It involves several steps and considerations to ensure the coal meets the desired specifications and requirements for its intended use. Designing a coal washing plant is a complex and strategic task that requires careful planning, technical expertise, and a focus on efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and safety.
The first step in designing a coal washing plant is to thoroughly characterize the coal to be processed. This involves analyzing its composition, ash content, moisture content, sulfur content, and other parameters that impact its quality and usability. Detailed analysis helps in determining the appropriate washing process and equipment required.
Once the coal is characterized, a process flow diagram is developed to outline the washing process. The PFD serves as a blueprint for the plant design, illustrating the various steps involved and their sequence. It also highlights the equipment required at each stage.
Based on the PFD and coal analysis, suitable equipment is selected for each stage of the washing process. Different equipment types such as crushers, screens, dense medium separators, jigs, and flotation cells are used based on the coal’s characteristics and the desired product quality.
The next step involves designing the layout of the coal washing plant. This includes arranging the equipment in a logical sequence and considering factors such as material flow, accessibility for maintenance, and safety of personnel.
Coal washing generates a significant amount of wastewater and requires a robust water management system. Designers must consider water recycling, treatment, and responsible discharge to minimize environmental impact.
Safety is of paramount importance in any industrial facility, and a coal washing plant is no exception. The design must adhere to safety standards and incorporate features to protect workers from potential hazards.
A well-designed coal washing plant should have operational flexibility to adapt to changes in coal quality, feed rate, and other factors. This allows the plant to maintain optimal efficiency and product quality under varying conditions.
Before proceeding with construction, it is essential to conduct an environmental impact assessment to evaluate potential effects on the surrounding ecosystem. Mitigation measures should be incorporated into the design to minimize adverse impacts.
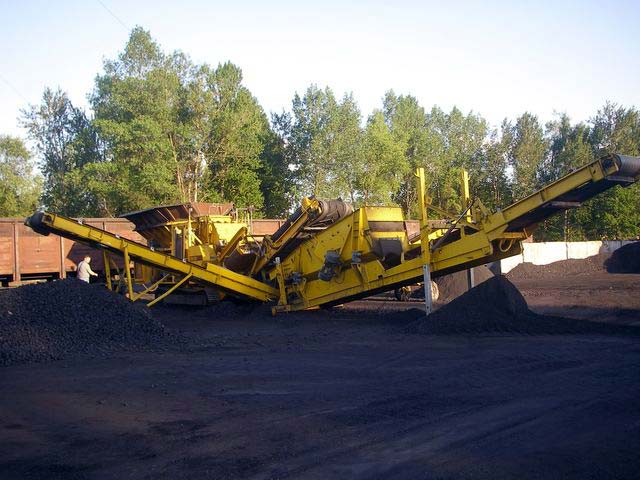

Different coal types have varying characteristics, such as particle size, density, and ash content. The equipment selected must be capable of handling the specific coal type and effectively separate impurities to achieve the desired product quality.
The capacity of the washing plant should align with the mine’s production capacity to ensure smooth operations. Choosing equipment with the right throughput capacity is vital to avoid bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
Some coal washing processes are more efficient at removing specific impurities than others. Designers must consider the trade-offs between various washing methods to achieve the desired level of coal purity.
The energy consumption of the equipment is a significant factor in determining the overall operating cost of the coal washing plant. Opting for energy-efficient equipment can lead to substantial cost savings in the long run.
The reliability of the equipment is crucial in maintaining uninterrupted operations. Equipment that is easy to maintain and has a proven track record of reliability should be prioritized.
The initial capital investment and ongoing operating costs play a vital role in the plant’s economic viability. A careful cost-benefit analysis should be conducted to choose equipment that offers the best balance between cost and performance.
The available space at the mine site may limit the size and number of equipment units that can be installed. Compact and efficient equipment designs are advantageous in such scenarios.
Some equipment and processes may generate more emissions or waste than others. Designers should select equipment that complies with environmental regulations to avoid potential fines and penalties.
Our Projects
Copyright © ZENITH, All Right Reserved.