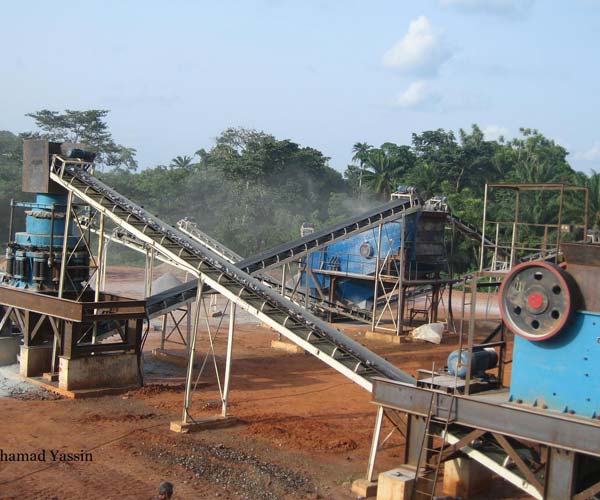
Limestone crushing plants hold immense significance in the extraction and processing of limestone, a resource that has shaped civilizations and industries alike. These plants are the cornerstone of transforming raw limestone into crushed forms tailored to meet specific requirements across construction, manufacturing, agriculture, and more.
24 Online Service

Limestone, a sedimentary rock composed primarily of calcium carbonate,limestone’s versatile properties have made it an essential element in various industries. One of the key steps in harnessing its potential lies in limestone crushing plants. These plants play a critical role in the extraction and processing of limestone, transforming raw material into various sizes of crushed limestone that meet specific requirements for construction, manufacturing, and beyond.
Limestone’s significance cannot be understated. Its wide range of applications spans construction, agriculture, manufacturing, and environmental sectors. In construction, it’s used as a primary building material for roads, bridges, buildings, and monuments. As an agricultural supplement, limestone corrects soil acidity and promotes healthy plant growth. In manufacturing, it’s a crucial component in cement, glass, and various chemicals. Moreover, limestone is pivotal in mitigating environmental issues, such as reducing emissions from power plants and treating polluted water.
The journey of limestone from its natural state to its versatile forms involves a series of carefully orchestrated processes. The starting point is the extraction of limestone from quarries or mines. These sites are carefully chosen based on factors like quality, accessibility, and environmental impact. Extraction methods can vary, ranging from open-pit mining to underground mining, each chosen based on geological and logistical considerations.
Once extracted, the raw limestone must undergo several stages of processing before it becomes a useful product. Among these stages, limestone crushing plants play a pivotal role. These plants use equipment like jaw crushers, impact crushers, and hammer mills to crush the limestone into smaller, uniform pieces. The crushing process facilitates proper calcination, a chemical transformation necessary to convert limestone into lime, an important component in many industrial processes.
Limestone crushing plants transform raw limestone into various sizes of crushed limestone to meet specific requirements. The process involves several stages:
In this initial stage, large chunks of limestone are fed into the jaw crusher, which applies mechanical force to break them into smaller pieces. This process reduces the raw material to a manageable size.
The crushed limestone obtained from primary crushing is further reduced in size using secondary crushers like impact crushers or cone crushers. These crushers refine the material to achieve the desired size range.
After secondary crushing, the crushed limestone is screened to separate it into different size fractions. This sorting process ensures that each fraction meets precise specifications for various applications.
Depending on the desired final product, some limestone crushing plants include a tertiary crushing stage. This further reduces the material size and ensures uniformity.
Crushed limestone comes in various sizes, each serving a specific purpose across diverse industries. For instance:
Different construction projects require different aggregate sizes. Crushed limestone is used as a base material for roads, driveways, and foundations, providing stability and support.
Crushed limestone is a key ingredient in cement manufacturing. It’s combined with other materials in precise proportions to create the necessary chemical reaction during the kiln process, resulting in the production of cement.
Crushed limestone is utilized in the production of glass, ceramics, and chemicals. Its chemical composition makes it a valuable raw material in various industrial processes.
Limestone that has been crushed to a fine powder is used to amend soil acidity and improve crop yields, supporting sustainable agriculture.

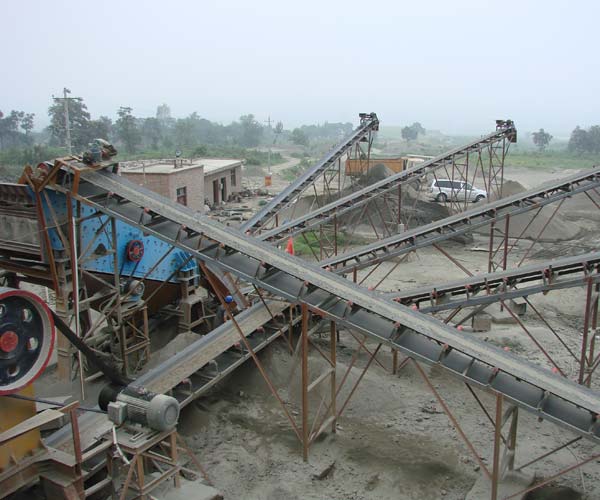
In the realm of industrial processes, the crushing of limestone stands out as a significant and indispensable activity. Limestone, a sedimentary rock composed primarily of calcium carbonate, is a key ingredient in various industries, from construction to agriculture. Its versatility and widespread use make the process of limestone crushing a crucial facet of modern development. Behind the scenes of this essential operation lies a complex machinery setup known as a limestone crushing plant.
Crushing is an essential process in various industries, converting large raw materials into smaller, manageable sizes for further utilization. One of the significant players in this process is limestone – a versatile rock used in construction, manufacturing, agriculture, and more.
The journey of limestone through a crushing plant commences with the primary crushing stage. This stage is crucial as it sets the foundation for subsequent stages, shaping the material for further processing. At this stage, the aim is to reduce the size of the raw limestone to a manageable size that can be handled by downstream equipment. The primary crusher plays a pivotal role in accomplishing this task.
These crushers are known for their robust construction and high crushing ratio. The mechanism involves a fixed jaw and a movable jaw, wherein the raw limestone is compressed between them. The advantages of jaw crushers lie in their simple design, ease of maintenance, and the ability to handle a wide range of materials.
These crushers utilize impact forces to crush the material. They consist of a rotor and hammers that strike the limestone, breaking it into smaller pieces. Impact crushers are efficient for primary crushing due to their high capacity and ability to produce cubical-shaped aggregates.
Following primary crushing, the limestone enters the secondary crushing stage. Here, the material is further reduced in size, enhancing its suitability for various applications. Secondary crushing not only improves product quality but also increases the options for utilizing the material.
These crushers are popular for their ability to produce finely crushed material. Cone crushers utilize a rotating mantle and an eccentrically gyrating head to compress the limestone against a concave surface. They offer excellent particle shape and are ideal for producing high-quality aggregates.
In the secondary stage, impact crushers can still be employed to refine the crushed material. Their versatility makes them suitable for various applications.
In some cases, tertiary crushing might be necessary to achieve specific product requirements. Tertiary crushers provide further refinement to the crushed limestone, tailoring it for niche applications that demand superior quality and precision.
VSI crushers are known for their ability to produce finely crushed, well-shaped aggregates. They work by accelerating the limestone into a high-velocity impact chamber, where it is shattered against an anvil or autogenous rock shelf.
HPGRs are relatively new players in the tertiary crushing scene. They use two counter-rotating rolls to crush the material, creating a more energy-efficient process with reduced fines generation.

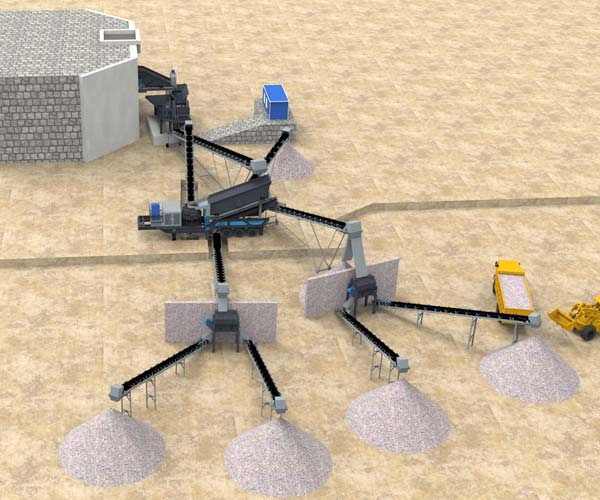
Once the limestone has been crushed to the desired size, it moves on to the screening stage. Screens are pivotal components of a crushing plant, responsible for segregating the crushed material into different sizes for further processing or direct use.
These screens use vibration to separate the crushed limestone into various sizes. Different decks and screen media can be utilized to achieve specific size fractions, making these screens highly adaptable to the production requirements.
In a limestone crushing plant, the conveyors play an essential role in transporting the crushed material between different stages of processing. They serve as the arteries of the operation, facilitating the efficient movement of material from crushers to screens and eventually to storage areas.
These are commonly used conveyors that utilize a continuous loop of fabric belts to move material. They are robust and capable of handling heavy loads, making them an ideal choice for the transport of crushed limestone.
Storage areas within a limestone crushing plant are vital for maintaining a steady supply of material to downstream processes. These areas act as buffers, allowing for continuous operation of the crushers and screens even when there is a temporary disruption in the supply of raw limestone.
Crushed limestone is often stored in stockpiles to ensure a consistent feed to the rest of the processing plant. These stockpiles are typically organized based on different product sizes and can be reclaimed using various equipment, such as loaders or reclaim feeders.
These structures store a smaller quantity of crushed limestone and are often strategically placed to feed specific processes. Bins and hoppers can help regulate the flow of material and ensure a consistent supply to downstream equipment.
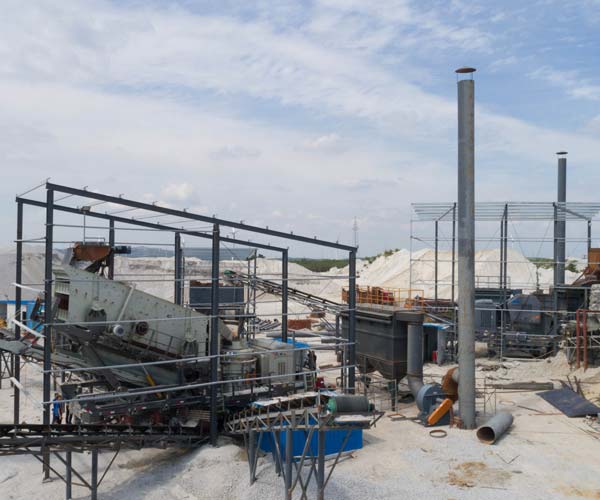
Limestone crushing plants often implement measures to control dust and minimize environmental impacts. Dust suppression systems using water sprays or misting nozzles can be installed to prevent the spread of airborne particles during the crushing process. Additionally, effective ventilation and dust collection systems are essential to maintain air quality and worker safety within the plant.
Our Projects
Copyright © ZENITH, All Right Reserved.